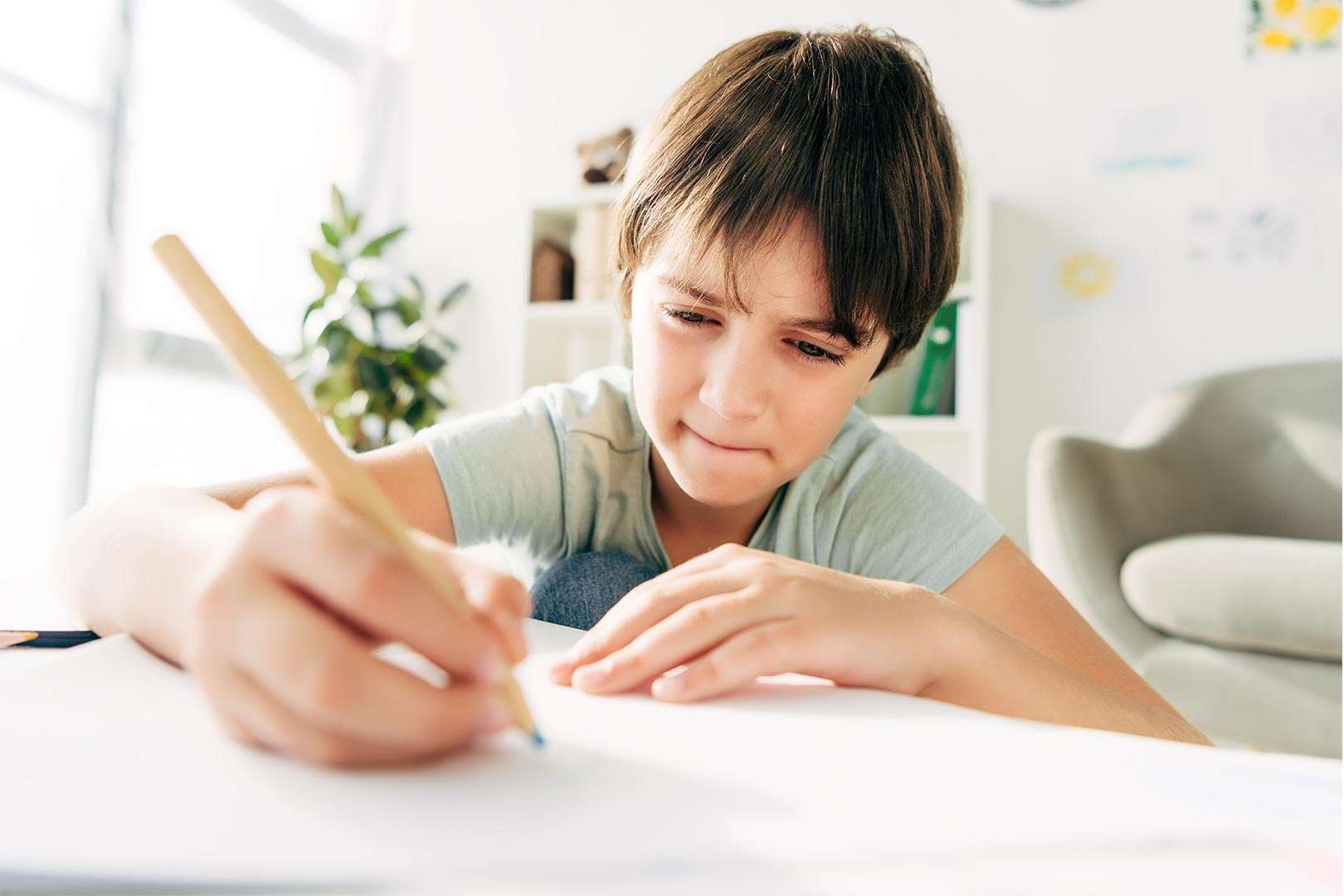
Dyslexia, a neurobiological condition characterized by difficulties with reading and spelling, affects approximately 10-15% of the population. Despite its prevalence, many educators remain unfamiliar with the nuances of dyslexia and struggle to provide effective instruction to these students.
Understanding Dyslexia: Dispelling Myths and Misconceptions
Dyslexia is often mistaken for laziness or a lack of intelligence. However, it is important to understand that dyslexia is not a reflection of a student’s cognitive abilities. Instead, it is a result of differences in how the brain processes language. These differences can manifest in various ways, including:
- Difficulty decoding words
- Slow reading speed
- Poor spelling
- Difficulty with phonological awareness (understanding the sound structure of words)
Creating a Dyslexia-Friendly Classroom Environment
The classroom environment can significantly impact the learning experience of students with dyslexia. Here are some strategies to foster a supportive and inclusive learning environment:
- Minimize distractions: Provide a quiet, clutter-free workspace to reduce visual distractions.
- Use multisensory approaches: Engage multiple senses to enhance learning. For example, use audiobooks, manipulatives, and visual aids.
- Provide explicit instruction: Break down complex concepts into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Offer consistent feedback: Provide regular and constructive feedback to help students track their progress.
- Encourage self-advocacy: Empower students to communicate their needs and preferences.
Effective Teaching Strategies for Dyslexia
Several teaching strategies can be particularly beneficial for students with dyslexia:
- Structured literacy: A systematic approach to teaching phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension.
- Multisensory phonics: Emphasizes the connection between sounds, letters, and words.
- Assistive technology: Utilize tools such as text-to-speech software and audiobooks to support reading and writing.
- Accommodations: Provide modifications to tasks or assessments to help students demonstrate their understanding.
Collaboration and Support
Effective teaching for students with dyslexia requires a collaborative approach involving parents, educators, and specialists. Parents can provide valuable insights into their child’s strengths and challenges, while specialists can offer expertise in dyslexia assessment and intervention strategies.
Empowering Students with Dyslexia
Dyslexia can pose significant challenges, but it does not define a student’s potential. With appropriate support and effective teaching strategies, students with dyslexia can thrive academically and reach their full potential. By understanding the unique learning needs of these students, educators can create inclusive classrooms that foster success for all.